683. Partial matrix sum
The matrix of integers aij is given, where 1 ≤
i ≤ n, 1 ≤ j ≤ m. For all i, j compute the partial
sums
![]()
Input. The first line contains the matrix size n and m (1 ≤ n, m
≤ 1000). Then follows the description of the matrix aij (1 ≤ aij
≤ 1000): each of the next n
lines contains m integers.
Output. Print the matrix of
partial sums Sij: n rows with m integers each.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 5 1 2 3 4 5 5 4 3 2 1 2 3 1 5 4 |
1 3 6 10 15 6 12 18 24
30 8 17 24 35
45 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let à be the input
array, s be the array of partial sums. We shall fill the array s row
by row in increasing order, and within each row, we shall process the cells in
increasing order of columns. Assume that at this point, all values of the array
s are already computed up to s[i][j].
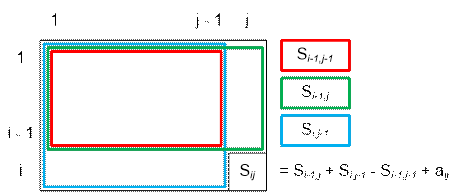
Then
s[i][j] = s[i – 1][j] + s[i][j – 1] – s[i – 1][j – 1] + aij
Example
Consider for the given example
how to compute the value of s[3][5].
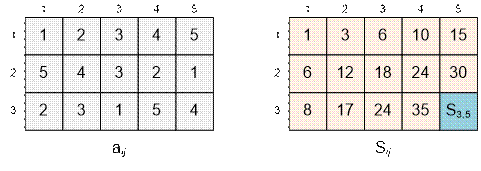
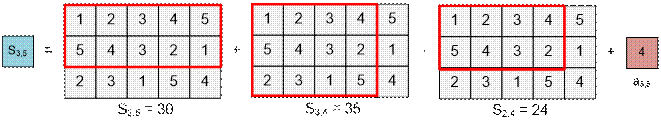
s[3][5] = s[2][5]
+ s[3][4] – s[2][4] + a35
= 30 + 35 – 24 + 4 = 45
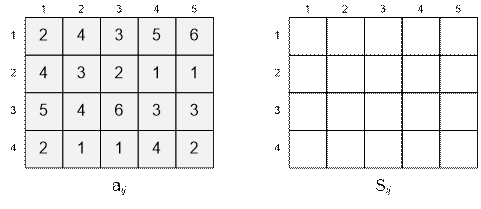
Exercise
For the given array aij compute the values of the elements in
the array sij.
Algorithm implementation
Declare two two-dimensional arrays.
#define MAX 1001
int a[MAX][MAX], s[MAX][MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= m; j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
Compute the partial sums.
memset(s,0,sizeof(s));
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= m; j++)
s[i][j] = s[i][j-1] + s[i-1][j] - s[i-1][j-1]
+ a[i][j];
Print the resulting array of partial sums.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j
<= m; j++)
printf("%d
",s[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
Algorithm implementation on fly
Read the next value aij,
immediately recompute and print the partial sum Sij. In this case, there is no need to store the input
array.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 1001
int i, j, n, m, value;
int mas[MAX][MAX];
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
memset(mas,0,sizeof(mas));
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&value);
mas[i][j] = mas[i][j-1] + mas[i-1][j] - mas[i-1][j-1] + value;
printf("%d ",mas[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}